 京公网安备 11010802034615号
经营许可证编号:京B2-20210330
京公网安备 11010802034615号
经营许可证编号:京B2-20210330
Python聚类算法之DBSACN实例分析
本文实例讲述了Python聚类算法之DBSACN。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
DBSCAN:是一种简单的,基于密度的聚类算法。本次实现中,DBSCAN使用了基于中心的方法。在基于中心的方法中,每个数据点的密度通过对以该点为中心以边长为2*EPs的网格(邻域)内的其他数据点的个数来度量。根据数据点的密度分为三类点:
核心点:该点在邻域内的密度超过给定的阀值MinPs。
边界点:该点不是核心点,但是其邻域内包含至少一个核心点。
噪音点:不是核心点,也不是边界点。
有了以上对数据点的划分,聚合可以这样进行:各个核心点与其邻域内的所有核心点放在同一个簇中,把边界点跟其邻域内的某个核心点放在同一个簇中。
# scoding=utf-8
import pylab as pl
from collections import defaultdict,Counter
points = [[int(eachpoint.split("#")[0]), int(eachpoint.split("#")[1])] for eachpoint in open("points","r")]
# 计算每个数据点相邻的数据点,邻域定义为以该点为中心以边长为2*EPs的网格
Eps = 10
surroundPoints = defaultdict(list)
for idx1,point1 in enumerate(points):
for idx2,point2 in enumerate(points):
if (idx1 < idx2):
if(abs(point1[0]-point2[0])<=Eps and abs(point1[1]-point2[1])<=Eps):
surroundPoints[idx1].append(idx2)
surroundPoints[idx2].append(idx1)
# 定义邻域内相邻的数据点的个数大于4的为核心点
MinPts = 5
corePointIdx = [pointIdx for pointIdx,surPointIdxs in surroundPoints.iteritems() if len(surPointIdxs)>=MinPts]
# 邻域内包含某个核心点的非核心点,定义为边界点
borderPointIdx = []
for pointIdx,surPointIdxs in surroundPoints.iteritems():
if (pointIdx not in corePointIdx):
for onesurPointIdx in surPointIdxs:
if onesurPointIdx in corePointIdx:
borderPointIdx.append(pointIdx)
break
# 噪音点既不是边界点也不是核心点
noisePointIdx = [pointIdx for pointIdx in range(len(points)) if pointIdx not in corePointIdx and pointIdx not in borderPointIdx]
corePoint = [points[pointIdx] for pointIdx in corePointIdx]
borderPoint = [points[pointIdx] for pointIdx in borderPointIdx]
noisePoint = [points[pointIdx] for pointIdx in noisePointIdx]
# pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in corePoint], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in corePoint], 'or')
# pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in borderPoint], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in borderPoint], 'oy')
# pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in noisePoint], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in noisePoint], 'ok')
groups = [idx for idx in range(len(points))]
# 各个核心点与其邻域内的所有核心点放在同一个簇中
for pointidx,surroundIdxs in surroundPoints.iteritems():
for oneSurroundIdx in surroundIdxs:
if (pointidx in corePointIdx and oneSurroundIdx in corePointIdx and pointidx < oneSurroundIdx):
for idx in range(len(groups)):
if groups[idx] == groups[oneSurroundIdx]:
groups[idx] = groups[pointidx]
# 边界点跟其邻域内的某个核心点放在同一个簇中
for pointidx,surroundIdxs in surroundPoints.iteritems():
for oneSurroundIdx in surroundIdxs:
if (pointidx in borderPointIdx and oneSurroundIdx in corePointIdx):
groups[pointidx] = groups[oneSurroundIdx]
break
# 取簇规模最大的5个簇
wantGroupNum = 3
finalGroup = Counter(groups).most_common(3)
finalGroup = [onecount[0] for onecount in finalGroup]
group1 = [points[idx] for idx in xrange(len(points)) if groups[idx]==finalGroup[0]]
group2 = [points[idx] for idx in xrange(len(points)) if groups[idx]==finalGroup[1]]
group3 = [points[idx] for idx in xrange(len(points)) if groups[idx]==finalGroup[2]]
pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in group1], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in group1], 'or')
pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in group2], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in group2], 'oy')
pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in group3], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in group3], 'og')
# 打印噪音点,黑色
pl.plot([eachpoint[0] for eachpoint in noisePoint], [eachpoint[1] for eachpoint in noisePoint], 'ok')
pl.show()
运行效果截图如下:
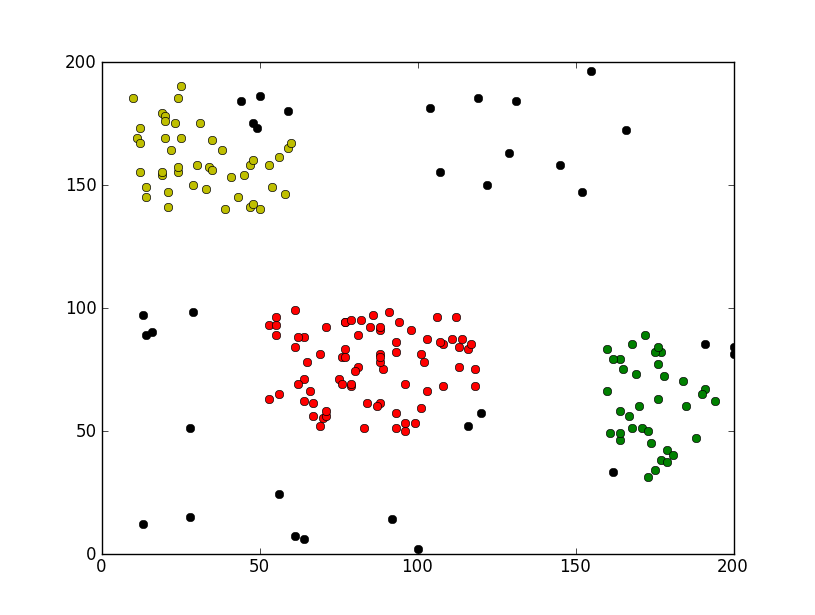
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。

数据分析咨询请扫描二维码
若不方便扫码,搜微信号:CDAshujufenxi
在日常办公中,数据透视表是Excel、WPS等表格工具中最常用的数据分析利器——它能快速汇总繁杂数据、挖掘数据关联、生成直观报表 ...
2026-02-28有限元法(Finite Element Method, FEM)作为工程数值模拟的核心工具,已广泛应用于机械制造、航空航天、土木工程、生物医学等多 ...
2026-02-28在数字化时代,“以用户为中心”已成为企业运营的核心逻辑,而用户画像则是企业读懂用户、精准服务用户的关键载体。CDA(Certifi ...
2026-02-28在Python面向对象编程(OOP)中,类方法是构建模块化、可复用代码的核心载体,也是实现封装、继承、多态特性的关键工具。无论是 ...
2026-02-27在MySQL数据库优化中,索引是提升查询效率的核心手段—— 面对千万级、亿级数据量,合理创建索引能将查询时间从秒级压缩到毫秒级 ...
2026-02-27在数字化时代,企业积累的海量数据如同散落的珍珠,若缺乏有效的梳理与分类,终将难以发挥实际价值。CDA(Certified Data Analys ...
2026-02-27在问卷调研中,我们常遇到这样的场景:针对同一批调查对象,在不同时间点(如干预前、干预后、随访期)发放相同或相似的问卷,收 ...
2026-02-26在销售管理的实操场景中,“销售机会”是核心抓手—— 从潜在客户接触到最终成交,每一个环节都藏着业绩增长的关键,也暗藏着客 ...
2026-02-26在CDA数据分析师的日常工作中,数据提取、整理、加工是所有分析工作的起点,而“创建表”与“创建视图”,则是数据库操作中最基 ...
2026-02-26在机器学习分析、数据决策的全流程中,“数据质量决定分析价值”早已成为行业共识—— 正如我们此前在运用机器学习进行分析时强 ...
2026-02-25在数字化时代,数据已成为企业决策、行业升级的核心资产,但海量杂乱的原始数据本身不具备价值—— 只有通过科学的分析方法,挖 ...
2026-02-25在数字化时代,数据已成为企业核心资产,而“数据存储有序化、数据分析专业化、数据价值可落地”,则是企业实现数据驱动的三大核 ...
2026-02-25在数据分析、机器学习的实操场景中,聚类分析与主成分分析(PCA)是两种高频使用的统计与数据处理方法。二者常被用于数据预处理 ...
2026-02-24在聚类分析的实操场景中,K-Means算法因其简单高效、易落地的特点,成为处理无监督分类问题的首选工具——无论是用户画像分层、 ...
2026-02-24数字化浪潮下,数据已成为企业核心竞争力,“用数据说话、用数据决策”成为企业发展的核心逻辑。CDA(Certified Data Analyst) ...
2026-02-24CDA一级知识点汇总手册 第五章 业务数据的特征、处理与透视分析考点52:业务数据分析基础考点53:输入和资源需求考点54:业务数 ...
2026-02-23CDA一级知识点汇总手册 第四章 战略与业务数据分析考点43:战略数据分析基础考点44:表格结构数据的使用考点45:输入数据和资源 ...
2026-02-22CDA一级知识点汇总手册 第三章 商业数据分析框架考点27:商业数据分析体系的核心逻辑——BSC五视角框架考点28:战略视角考点29: ...
2026-02-20CDA一级知识点汇总手册 第二章 数据分析方法考点7:基础范式的核心逻辑(本体论与流程化)考点8:分类分析(本体论核心应用)考 ...
2026-02-18第一章:数据分析思维考点1:UVCA时代的特点考点2:数据分析背后的逻辑思维方法论考点3:流程化企业的数据分析需求考点4:企业数 ...
2026-02-16